Volume Weight of Mattresses
In connection with the selection of a new mattress, one inevitably stumbles over the term “volume weight”.
What does density mean in mattresses?
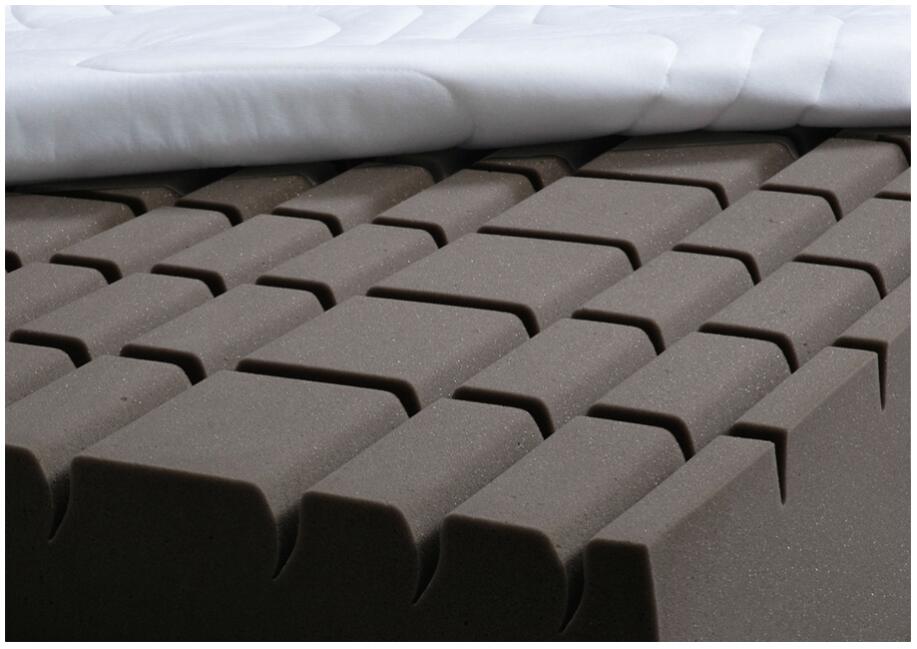
The volume weight is a physical parameter that provides information about the quality of a mattress. The density is mainly important for cold foam, visco foam, latex and gel mattresses.
When manufacturing mattress cores from foamed material, the volume weight expresses the mass (in kg) of one cubic meter (m³) of the foam used. The process of foaming ensures that tiny air pockets or pores are created in the raw material. In this way, the future mattress core will have positive properties in terms of ventilation and breathability. However, if the proportion of air in the core material is too high in relation to the actual foam, this has negative effects on the dimensional stability and thus, among other things, on the durability or service life of the mattress.
A low volume weight also has an influence on the resilience of the mattress, since the core material returns to its original shape only poorly and very slowly after loading. This can lead to (temporary) hollows. Conversely, mattresses with a high volume weight also have a very good resilience due to the associated high dimensional stability.
Mattresses with a high density have cores with a higher (raw) density and only a small pore volume. In mattresses with a lower density, the core is correspondingly more porous and has a lower (raw) density.
The volume weight is mainly abbreviated as RG – in some cases, RG is also referred to as the unit for the volume weight. In the product descriptions or detailed information on mattresses, information such as RG 40, RG 50 or RG 60 or complete RG 40 kg / m³, RG 50 kg / m³ or RG 60 kg / m³ can be found.
There is no specific relationship between the density and the firmness of the mattress: A mattress with a very high density of RG 75 does not have to be firmer than a cheap mattress in RG 20 or 25 in terms of the perceived feeling of lying on it. The so-called compression hardness is responsible for this. This is the force that has to be used to compress a raw foam block by 40% of its normal height. Since the compression hardness of incised cores cannot be traced, we work in the Betten.de online shop with specific information on the strength of our mattresses and do not specify values for the compression hardness.
The density of different types of mattresses cannot be compared directly with one another. For example, latex mattresses – especially mattresses with a core made of natural latex – always have a higher density than, for example, cold foam mattresses. This has to do with the fact that in the manufacture of latex cores for mattresses, significantly more material has to be used than in the manufacture of cores from cold foam.
How is the volume weight calculated?
The density of mattresses can easily be calculated using a formula. To do this, the variables weight of the mattress in kilograms (kg) and the volume of the mattress in cubic meters (m³) must be known.
Calculation of the volume weight in individual steps:
- Determining
the mattress weight You can find out the weight of the mattress by weighing the core. To do this, you have to remove the cover from the mattress (see information in the information box below). It is a little easier if you know the total weight of the mattress (usually stated on the packaging). Then you just have to weigh the cover and then subtract the weight of the cover from the total weight. - Calculating the mattress volume
Multiply the length by the width and height of the mattress or the mattress core (length x width x height). - Calculate
volume weight Divide the mattress weight by the volume to get the volume weight.
Important information on calculating the density of mattresses
- When calculating the volume weight, it is only about the dimensions of the mattress core. The cover, which on some mattresses can be 2 cm and higher, must not be included in the calculation.
- Incisions in the mattress core reduce the material and weight of the core. For this, a tolerance of +/- 10% should generally be taken into account when calculating the volume weight.
How high should the density of a mattress be?
There are general statements about how long mattresses and what density can be kept (see table in the information box). The durability of a mattress also depends on other factors than the volume weight, so you should only see the general statements on the service life in years as a rough guide.
Volume weight and durability of mattresses
| RG 20 to RG 25: | Low standard | Shelf life: about 1-2 years |
| RG 30: | Standard | Shelf life: about 2-3 years |
| RG 35: | Higher standard | Shelf life: about 5-6 years |
| RG 40: | Good quality | Shelf life: about 6-8 years |
| RG 50 to RG 60: | Very high quality | Shelf life: about 10 years |
| RG 75: | Excellent quality | Shelf life: over 10 years |
In our experience, a good quality mattress should have a density of at least 40, which, by the way, corresponds to DIN 13014 for mattresses in hospitals and also corresponds to the ou recommendations.
If you want to purchase a foam mattress for the rarely used guest bed or as a mattress in the cot, a density of 20-30 is usually sufficient due to the lower load.